COMISAIR 7-Year Study Shows Significant A1C Reduction and TIR Increase with rtCGM Compared to CBG

The COMISAIR 7-year study is the longest prospective real-world rtCGM study ever conducted. Preliminary results presented at EASD show using a real-time continuous glucose monitoring system (rtCGM), like Dexcom G7, can significantly and continuously reduce A1C for people living with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
7-Year Study Shows Prolonged Benefits of rtCGM
As the longest, most comprehensive rtCGM study to date, the COMISAIR data provides exciting new insights for the future of diabetes care.
The study followed 94 patients living with T1D with baseline A1C levels between 7 and 10 percent. All participants in the rtCGM study cohort agreed to use their Dexcom rtCGM device more than 70% of the time.1
The most recent results show that participants experienced significantly lower A1C levels when using rtCGM. Additionally, their A1C continued to decrease over the course of the study period.
rtCGM is More Effective Compared to CBG
The study found that over seven years, real-time continuous glucose monitoring has had greater and statistically significant A1C reductions compared to capillary blood glucose (CBG) monitoring. This is regardless of the insulin delivery method, multiple daily injections or insulin pump therapy.
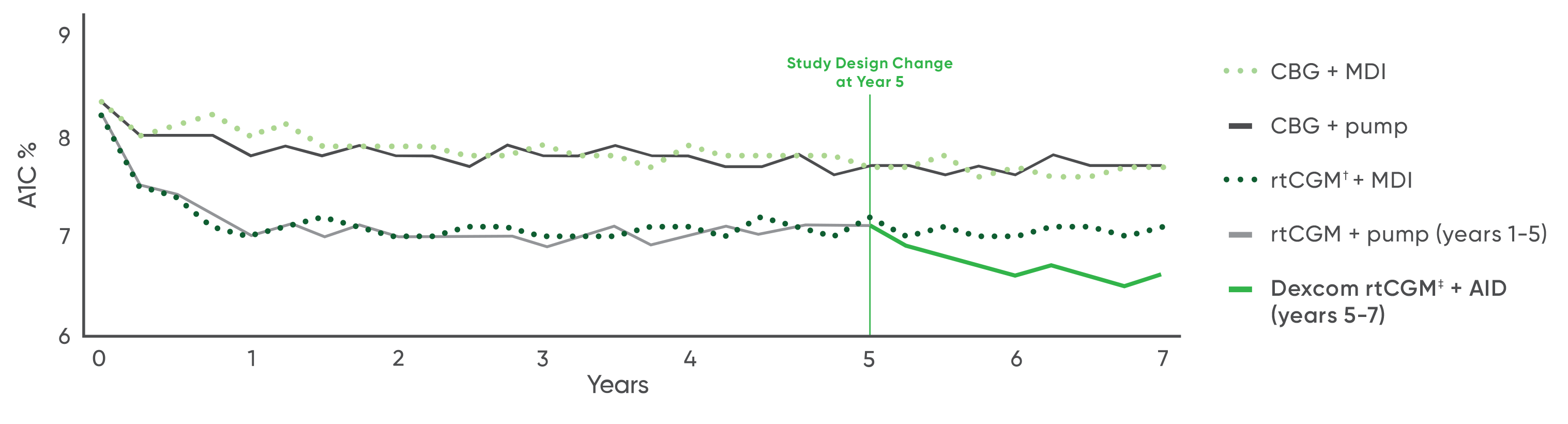
Additionally, on average, those using rtCGM were able to achieve target time in range (3.9-10mmol/L)2 greater than 70%, and were half as likely to have developed new or progressive diabetic retinopathy (DR).
These results indicate that rtCGM is more effective at managing blood glucose levels than traditional capillary blood glucose (CBG) monitoring, with sustained long-term benefits.
Additional Benefits When rtCGM is Used With AID System
Results from the study also showed encouraging data on rtCGM-connected automated insulin delivery (AID) systems. It found that managing diabetes with a Dexcom rtCGM-powered AID system, specifically Tandem Diabetes Care Control IQ, lowered A1C more effectively than multiple daily injections.
rtCGM adherence was 91.9 percent at seven years—3.1 percent higher than those who used rtCGM with multiple daily injections instead.
Dexcom rtCGM Improves Long-Term Diabetes Care
The COMISAIR 7-year study reaffirms the effectiveness of rtCGM, like the Dexcom G7, in lowering A1C and improving diabetes management. You can request samples of Dexcom G7 to better understand why rtCGM is an easy, effective tool for people living with T1D.
Read the summary of the COMISAIR study to dive deeper into the long-term benefits of rtCGM.
DR, diabetes retinopathy; EASD, European Association for the Study of Diabetes; TIR, time in range.
1 Soupal J. Comparison of Different Treatment Modalities in 7 Years of Follow-up. Presented at: EASD 2023; October 2, 2023; Hamburg, Germany.
2 Battelino T, et al. Diabetes Care 2019;42(8):1593-1603. doi: 10.2337/dci19-0028.
MAT-2261 V1.0
