A wide body of evidence substantiates the efficacy of Dexcom Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems for insulin-using patients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes (T1D/T2D).

Reduction of A1C by 1.0% for Patients with T1D
Dexcom CGM System users on a multiple daily injections (MDI) insulin regimen showed an average A1C reduction of 1% after 24 weeks of regular use, compared to baseline. Additionally, 52% of subjects in the study had a ≥1% A1C reduction.*,1

Significant A1C Reduction for Patients with T2D
Patients with T2D on mealtime insulin achieved an average 1.4% A1C reduction after using Dexcom G6 for 12+ weeks.†,2

Increased Time in Range
In a trial where Dexcom G6 powered a hybrid closed-loop insulin pump system, participants with T1D increased their time in range (TIR) by an average of 2+ hours per day.3
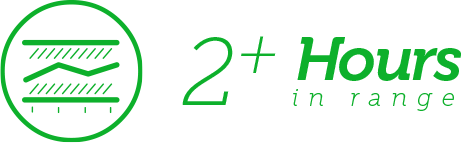
Improvement in Quality of Life
Patients with T2D on mealtime insulin experienced significant quality of life (QOL) score improvements after starting Dexcom G6.†,2

* Study conducted in the United States using the Dexcom G4® PLATINUM CGM System with 505 Software, which uses the same software as the Dexcom G5® Mobile CGM System in Canada.
† Prior to participating in any study procedures, each subject was asked to voluntarily document their consent by signing an Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved informed consent form.
1. Beck RW, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378.
2. Gilbert TR, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S1):S35-S39.
3. Kovatchev B, et al. N Engl J Med 2019;381(18):1707-1717.
4. Šoupal J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2019;43(1):37-43.
