Canadian Study Associates rtCGM with A1C, TIR, and Glycemic Variability Improvements
A new study conducted using the Canadian LMC Diabetes Registry has shown that real-time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (rtCGM) can significantly reduce A1C levels in people living with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The study found that rtCGM leads to better blood glucose control and reduced glycemic variability, and that rtCGM is more effective than intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) in increasing time in range (TIR)1.
This study emphasizes the potential of rtCGM to improve glucose control in the real world, not just in a controlled clinical study setting. rtCGM has been shown to be an effective tool for people living with T1D2-4, and this new data underscores the importance of rtCGM in improving patient outcomes.

About the Canadian LMC Diabetes Registry study
The REAL-CGM-T1D study was a retrospective observational analysis that investigated real-world clinical outcomes at 6–12 months in adults with T1D who initiated a rtCGM device, and compared these clinical outcomes to a matched cohort of participants who initiated an isCGM device. 1,612 adults were reviewed and matched for age, sex, diabetes duration, A1C, and insulin delivery method. Patients consented to have their medical records used for research purposes and an independent ethics committee approved the protocol. All outcomes were evaluated at baseline and during follow-up.
How it differs from prior CGM studies
Previous comparative studies of rtCGM vs. isCGM in adults with T1D5 have associated rtCGM with significantly less time spent in hypoglycemia and significantly more time in range (TIR) compared to isCGM. However, the effectiveness of rtCGM vs. isCGM on A1C and CGM metrics has not been studied in a way that compares the two types of devices to each other while using matched groups of participants.
"To our knowledge, this is the first study to compare HbA1C and CGM metrics in a matched cohort of participants with T1D who initiated a rtCGM or an isCGM device during real-world clinical practice. The 6–12 month follow-up period is also a strength of this study, as it shows the longer term real-world glycemic effects of initiating these devices."
Study Results
The study found that, compared to a matched comparator group of adults with T1D who started using an isCGM device, those who started using a rtCGM system had significantly lower A1C levels, spent more time in range, and had lower glycemic variability than their isCGM counterparts.
The results of this study concluded that:
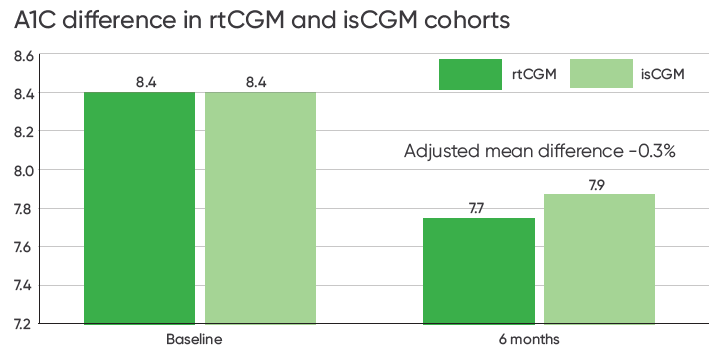
rtCGM Was Associated with Significantly Reduced A1C1
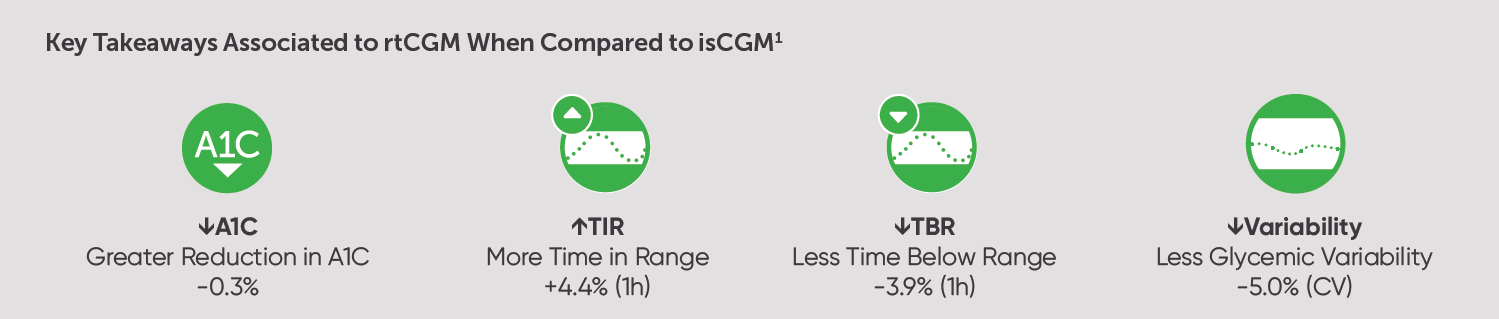
The study found that rtCGM was associated with greater reductions in A1C compared to isCGM. rtCGM users had a statistically significantly greater reduction in A1C (-0.7%) compared to the isCGM cohort (-0.5%).
Adjusted mean difference between matched cohorts was -0.3% [p=0.01, 95% CI, −0.5 to −0.1].
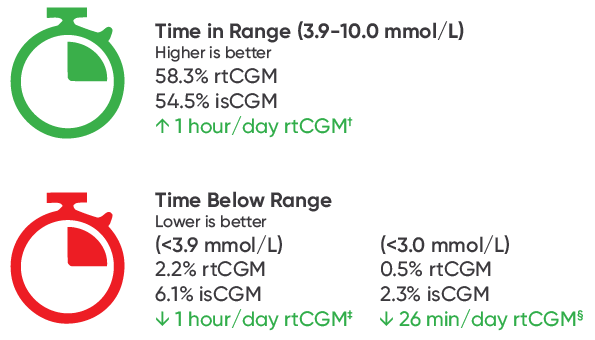
rtCGM Was Associated with Significantly Improved TIR1
The study also found that rtCGM users had significantly higher time in range (+1 hour/day) and significantly lower time below range <3.9 mmol/L (-1 hour/day) compared to isCGM users.
Adjusted mean difference between matched cohorts was 4.4% (95% CI [0.4 to 8.3], p=0.03), and -3.9% (95% CI [-4.9 to -2.8], p<0.001) respectively.
rtCGM Users Had Lower Glycemic Variability1
In addition, rtCGM users in the study had significantly lower glycemic variability (CV 34.3%) compared to isCGM users (CV 39.3%) at follow up.
Adjusted mean difference between matched cohorts was -5.0% [p<0.001, 95% CI, -6.9 to –3.2].
Download Results Summary (PDF)
Further Support for rtCGM
The results of this study have associated rtCGM with reduced A1C, improved time in range, and reduced glycemic variability. This is especially true for Canadians living with type 1 diabetes on intensive insulin therapy (IIT) who are at higher risk for hypoglycemia.
In addition, rtCGM products like Dexcom G6 are now supported by the latest Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPG).6 rtCGM systems are also recommended by leading international diabetes organizations, such as the American Diabetes Association (ADA)7, and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology8.
Get your patients started on Dexcom G6 today. Learn more about available healthcare coverage, or contact our dedicated team of specialists for support.
LBL-1002179 Rev001
1 Brown R, et al. Diabetic Medicine. 2022;39(11):e14937.
2 Beck RW, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371–378.
3 Thabit H, et al. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(10):2537-43.
4 SENCE Study Group. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(2):464-472.
5 Visser MM, et al. Lancet. 2021;397(10291):2275-2283.
6 Cheng A, et al. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(Suppl 1):S1-S325.
7 American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(Suppl 1):S85–S99.
8 Grunberger G, et al. Endocrine Practice. 2021;27(6):505–537.
